News Story
White Group Sensors Paper a Royal Society of Chemistry Hot Pick
A new paper by Fischell Department of Bioengineering (BioE) assistant professor Ian White and BioE graduate student Wei W. Yu has been promoted by Analyst, the Royal Society of Chemistry's analytical and bioanalytical research journal.
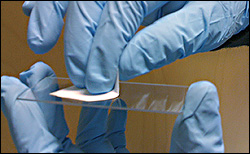
The work documents the latest developments in the White Group's paper-based surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (P-SERS) research, which uses ordinary inkjet printers and nanoparticle-laced ink to print sensitive, portable and inexpensive biosensors. Normally, a sample would need to be collected and pipetted onto a sensor's surface, but White and Yu describe how the natural capillary action of the paper transforms it into a swab or a dipstick, making liquid sample collection easier and more flexible. Once absorbed by the paper, the fluid sample can be directed to specific areas of the sensor using lateral flow. In testing, the P-SERS dipsticks and swabs were able to detect trace amounts of drugs, dyes and pesticides measured in mere picograms and nanograms.
"Inkjet-Printed Paper-Based SERS Dipsticks and Swabs for Trace Chemical Detection," is available free online for a limited time, and will be featured a the print edition's cover story in a future issue.
For More Information:
Visit the White Group web site »
Published September 20, 2012